• To define Automation and Control and explain the differences in the sense of the terms
• To explain the relation between Automation and Information Technology
• To underline the basic objectives of a manufacturing industry and explain how automation and control technologies relate to these
• To introduce the concept of a Product Life Cycle and explain how Automation and Control technologies relate to the various phases of the cycle
• To classify Manufacturing plants and categorise the different classes of Automation Systems that are appropriate for these Understanding the Title of the Course Let us first define the three key words in the title, namely
Industry
In a general sense the term “Industry” is defined as follows. Definition: Systematic Economic Activity that could be related to Manufacture/Service/ Trade.
Automation
The word ‘Automation’ is derived from greek words “Auto”(self) and “Matos” (moving).
Automation therefore is the mechanism for systems that “move by itself”. However, apart from this original sense of the word, automated systems also achieve significantly superior performance than what is possible with manual systems, in terms of power, precision and speed of operation.
Definition: Automation is a set of technologies that results in operation of machines and systems without significant human intervention and achieves performance superior to manual operation A Definition from Encyclopaedia Britannica The application of machines to tasks once performed by human beings or, increasingly, to tasks that would otherwise be impossible. Although the term mechanization is often used to refer to the simple replacement of human labour by machines, automation generally implies the integration of machines into a selfgoverning system.

Control
It is perhaps correct to expect that the learner for this course has already been exposed to a course on Control Systems, which is typically introduced in the final or pre-final year of an undergraduate course in Engineering in India. The word control is therefore expected to be familiar and defined as under. Definition: Control is a set of technologies that achieves desired patterns of variations of operational parameters and sequences for machines and systems by providing the input signals necessary.
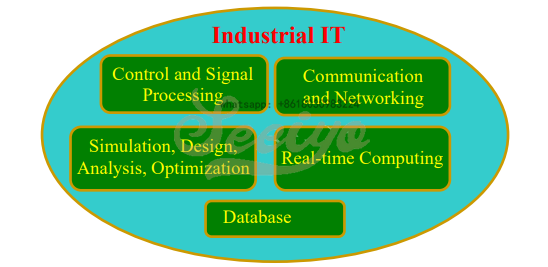
Industrial Automation vs. Industrial Information Technology
Industrial Automation makes extensive use of Information Technology. Fig. 1.1 below shows some of the major IT areas that are used in the context of Industrial Automation.
Summary
In this lesson we have dealt with the following topics:
A. Definition of Automation and its relations with fields of Automatic Control and Information Technology: It is seen that both control and IT are used in automation systems to realize one or more of its functionalities. Also, while Control Technology is used for operation of the individual machines and equipment, IT is used for coordination, management and optimized operation of overall plants.
B. The role played by Automation in realizing the basic goal of profitability of a manufacturing industry: It is seen that Automation can increase profitability in multiple ways by reducing labour, material and energy requirements, by improving quality as well as productivity. It is also seen that Automation is not only essential to achieve Economy of Scale, but also for Economy of Scope.
C. Types of Factories and Automation Systems that are appropriate for them: Factories have been classified into four major categories based on the product volumes and product variety. Similarly Automation Systems are also categorized into four types and their appropriateness for the various categories of factories explained.







